December 9, 2023
Grain elevators are used to store grain between when it is harvested and when it is sent to the point of use. They have been around in North America since 1842 when they were developed to store grain being transported via the Erie Canal. Some elevators are very large and communal in their function while some are also used for milling or personal applications on farms. In this post we share pictures we have taken of some of them in Ontario and Manitoba.
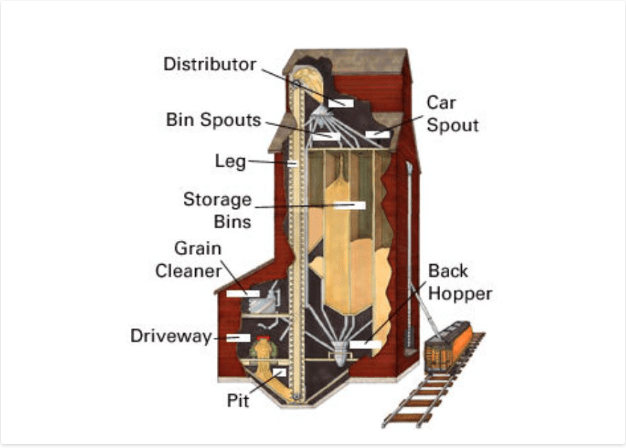
Elevators were made with a sturdy wooden crib built of 2 by 8 boards that then had 2 by 6 inch ones stacked up to form the walls and internal bins. The outside would be covered with a wooden veneer which was originally painted red if along a CPR line. Wheat can weigh up to 60 pounds per bushel which means that a 25,000 bushel elevator could have 1.5 million pounds (680,000 kgs) of weight in it. This puts a lot of lateral pressure on the walls. Eventually, elevators that would hold 60,000 bushels were constructed. All elevators, regardless of size, had three basic elements. The elevator, the driveway and the office/engine room. A truck or wagon of grain would be driven onto a scale and weighed and the grain sampled to see what quality it was. It would then be dumped through the floor into the pit where it would be taken up the leg and poured into the correct storage bin. The empty truck would then be weighed again and the amount of grain deposited would be calculated from the weight difference. When it was time to load a train the appropriate grain would be pumped into the back hopper and then down a spout into the waiting boxcar. The illustration below was taken from The Canadian Encyclopedia and shows the inner workings of a grain elevator.
The first grain elevator on the Canadian prairies was developed in Niverville, Manitoba in 1879 and was basically a grain silo. The more traditional shape started to appear in 1881 in the form of 25,000 bushel elevators. The CPR began to offer free land along their rail lines to allow the construction of standard size elevators. While on a recent business trip to Manitoba I was able to photograph the two grain elevators that appear next in this article.
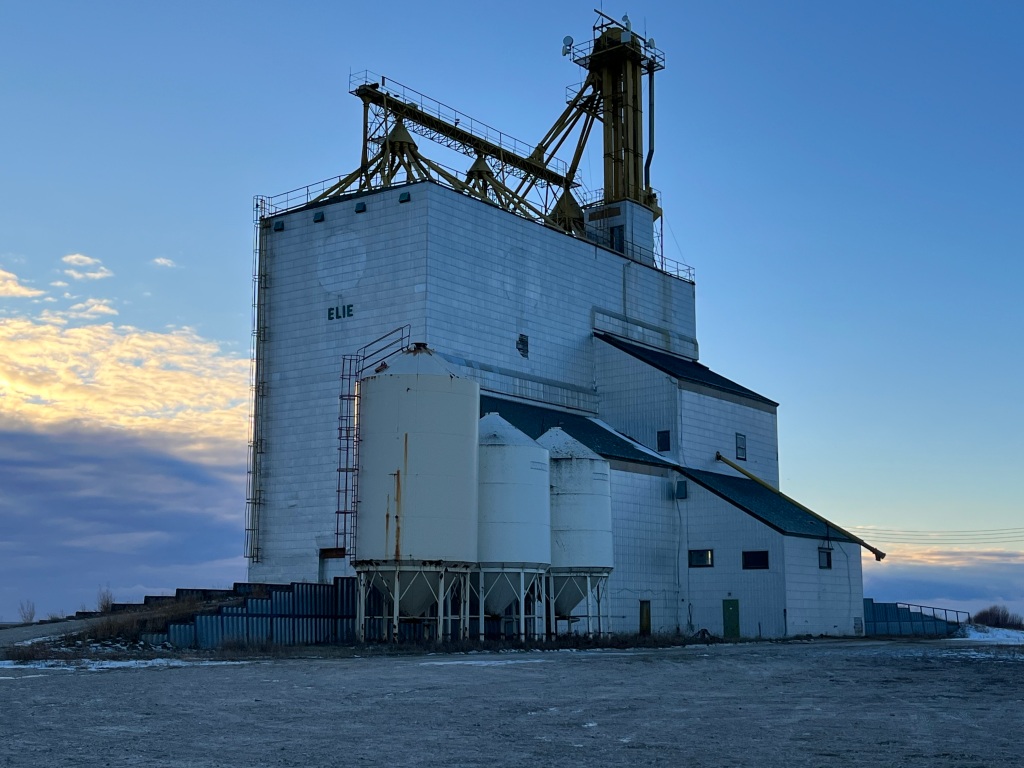
The United Grain Growers had built a grain elevator in Elie, Manitoba in 1928 which has since been demolished. A larger grain elevator was built just west of town in 1986 with a capacity of 3,750 tons. In 1998 the Manitoba Pool and Alberta Pool merged creating Agricore. The elevator was then closed in 2002 but has since been bought by some local farmers who continue to use it. Unlike the majority of elevators, this one has no direct rail access.

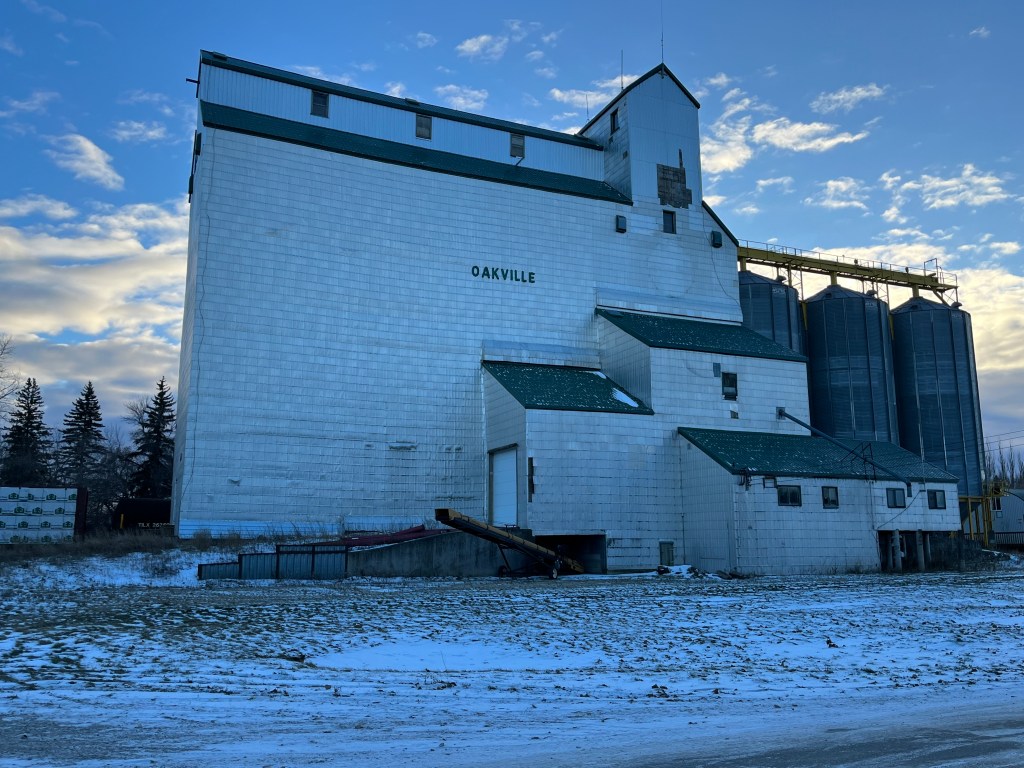
A little west of Elie is the town of Oakville, Manitoba. When their 1928 Pool B elevator burned down in December 1973 it was replaced with the present wooden structure. This building was completed between 1974 and 1975 and had a capacity of 162,000 bushels. It was expanded in 1990 by adding the three steel tanks on the west end that brought the capacity up to 204,000 bushels. When the merger happened in 1998 its days were numbered. It was closed in January 2001 as a temporary cost cutting measure by Agricore and permanently closed in November 2001. Like the elevator in Elie, it is now operated for private grain storage. It can be found at this map link.

The CPR built a line through Pontypool, Ontario in the 1880s which opened up the Toronto market to local farmers. In 1894 a grain elevator was built and before long there were two elevators serving the community of about 600 residents. Both of these were gone by 1918 and a new one was constructed for the local farmers to store their barley, oats and wheat before shipping it to market. As transportation systems improved the elevator became less important and by the 1970s it was closed. It can be found at this map link.

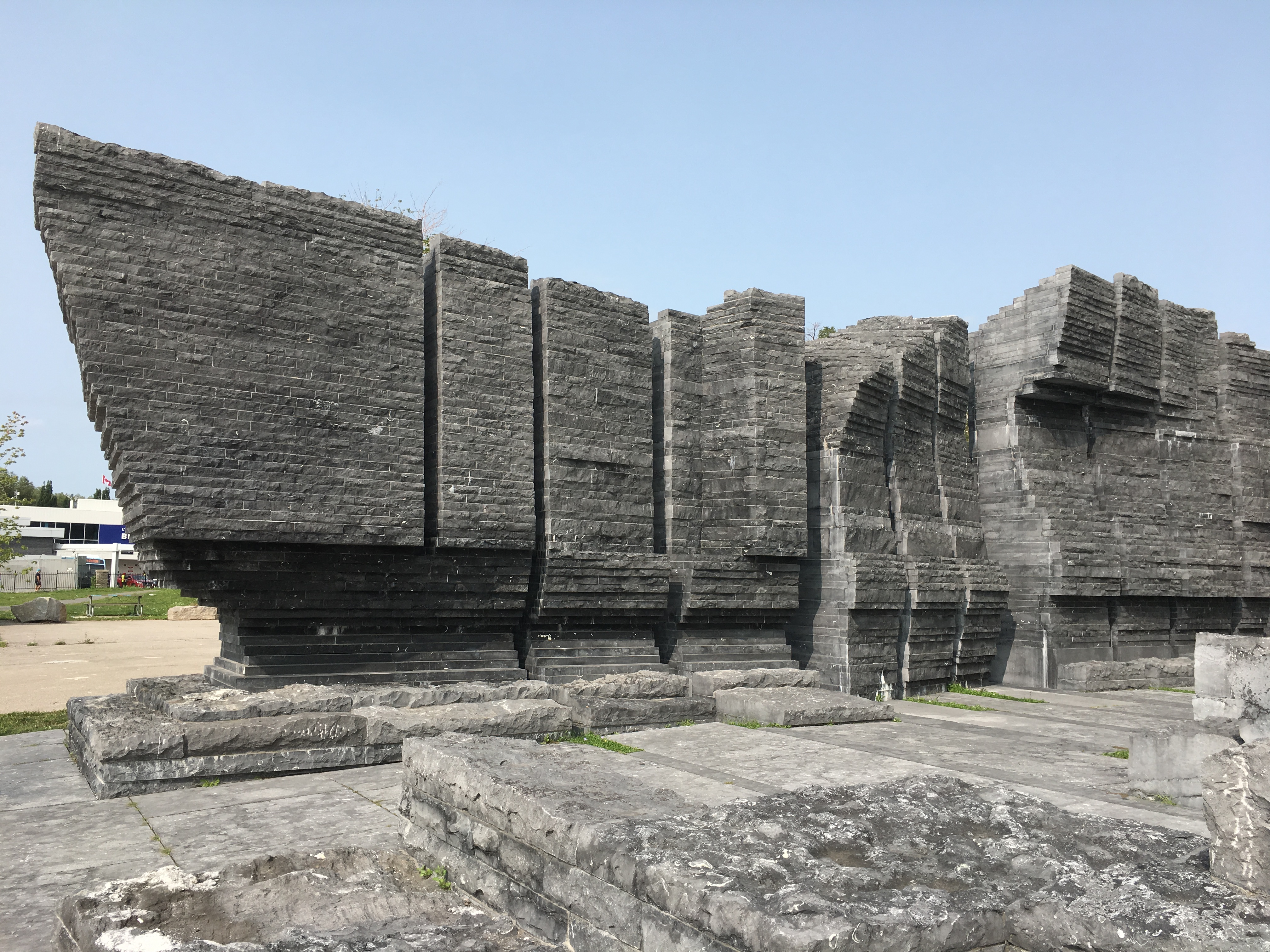
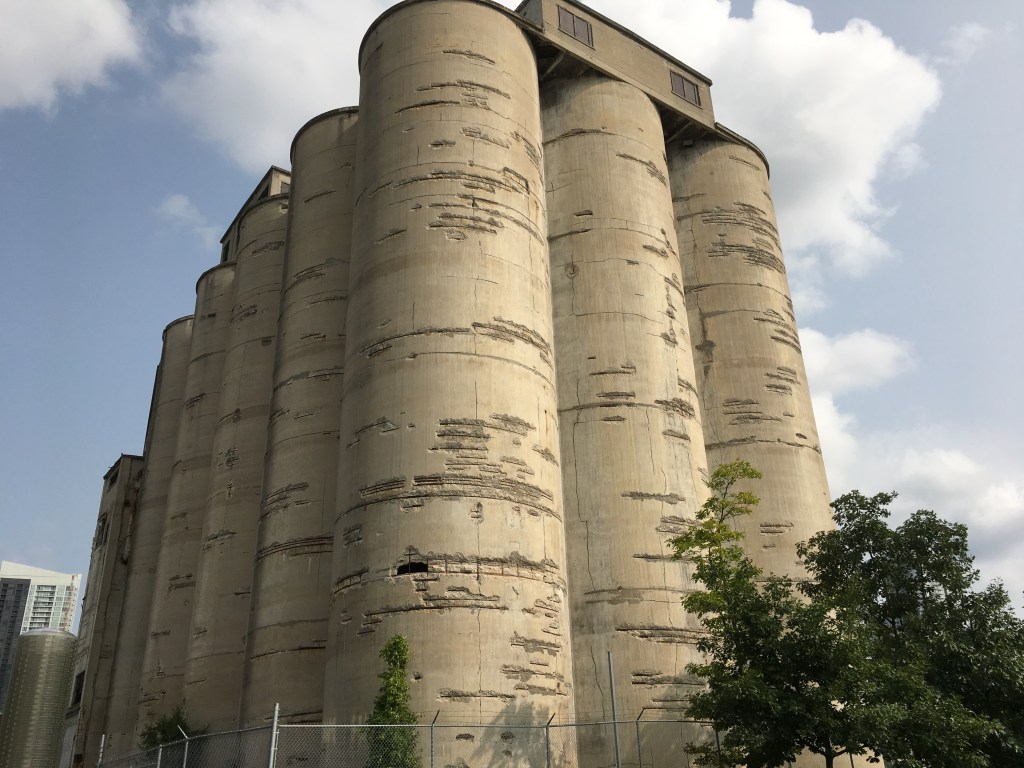
The Canada Malting Company located a set of concrete silos at the foot of Bathurst Street in 1928. Storage silos had disappeared from the city because they were made of wood and had a lifespan of about ten years due to the fact that they were severe fire hazards. The Canada Malting Company used concrete silos to store barley in before it was turned into malt. The original silos near the lake were 120 feet tall and more storage was added in 1944 in the form of 150-foot tall silos. These grain silos can be found at this map link.

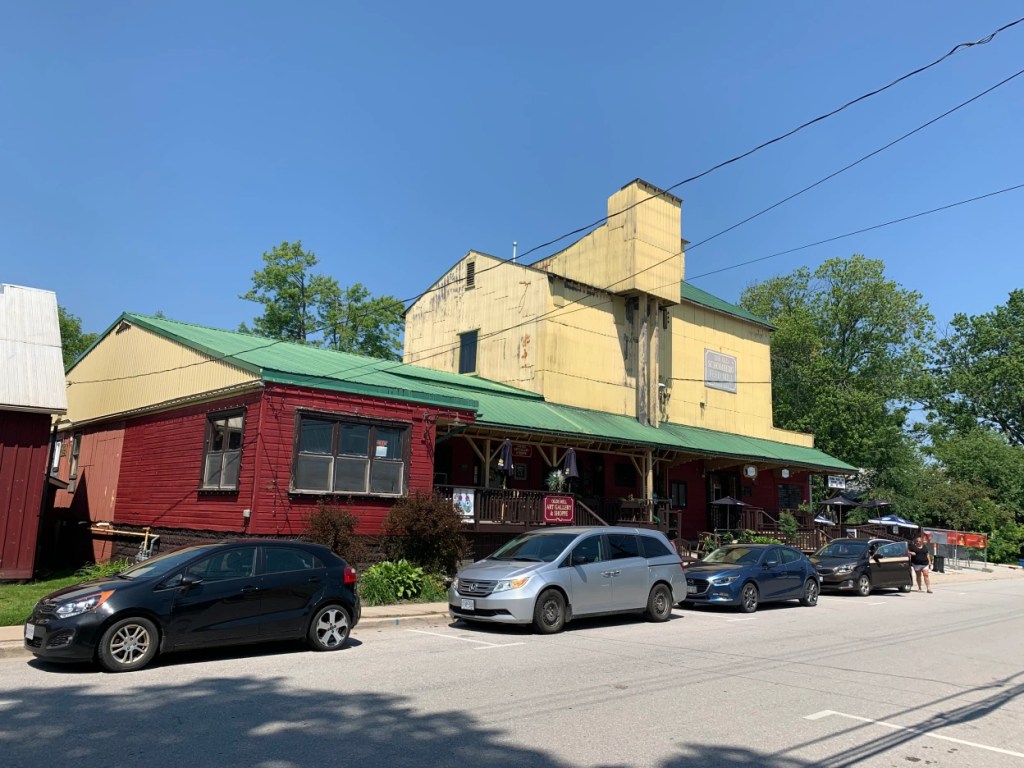
There are two grain elevators in the town of Schomberg, Ontario. In 1884 Anderson Tegart built the Schomberg Feed Mill on Main Street where it had direct access to the railway. It operated until 1927 before it shut down. Since that time it has housed a variety of businesses including The Scruffy Duck Restaurant which is still in business. This elevator can be found at this map link.

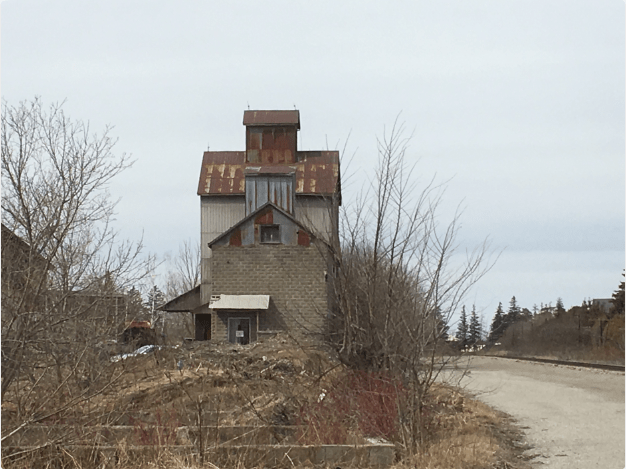
An orange grain elevator stands on the side of Highway 9 close to Highway 27 that used to have the Shur-Gain symbol on the side. Shur-Gain was introduced in 1937 as a brand name by Canada Packers. They provided feed for animals and livestock. Today there appears to be renovations going on at the old feed mill. This elevator can be found at the following map link.

I have driven through Consecon in Prince Edward Ontario several times on recent business trips and kept looking at the old grain elevator that stands beside the Millennium Trail on the old Price Edward County Railway. Yesterday I stopped to take pictures of the structure. The Consecon grist mill was built in 1808 and spurred development of the community. After several rebuilds it was purchased by Richard Baldwin in 1949. He built the grain storage building beside the tracks the same year. When rail service ended through town in 1985 the building was abandoned. It can be found at this map link.

Nashville, Ontario grew as a railway town centered on the railway station. Soon a saw mill and a grain elevator stood near the railway. Milling grain creates a lot of dust which becomes a fire hazard. Many grist mills and grain elevators were destroyed by fire and this was the fate of the original grain elevator in Nashville. The first elevator burned on July 15, 1919 while a second one was destroyed in 1927. A new grain elevator was built in Nashville in 1930 and still stands beside the tracks. We featured it in our post on Abandoned Kirby Road and it can be found at this map link.

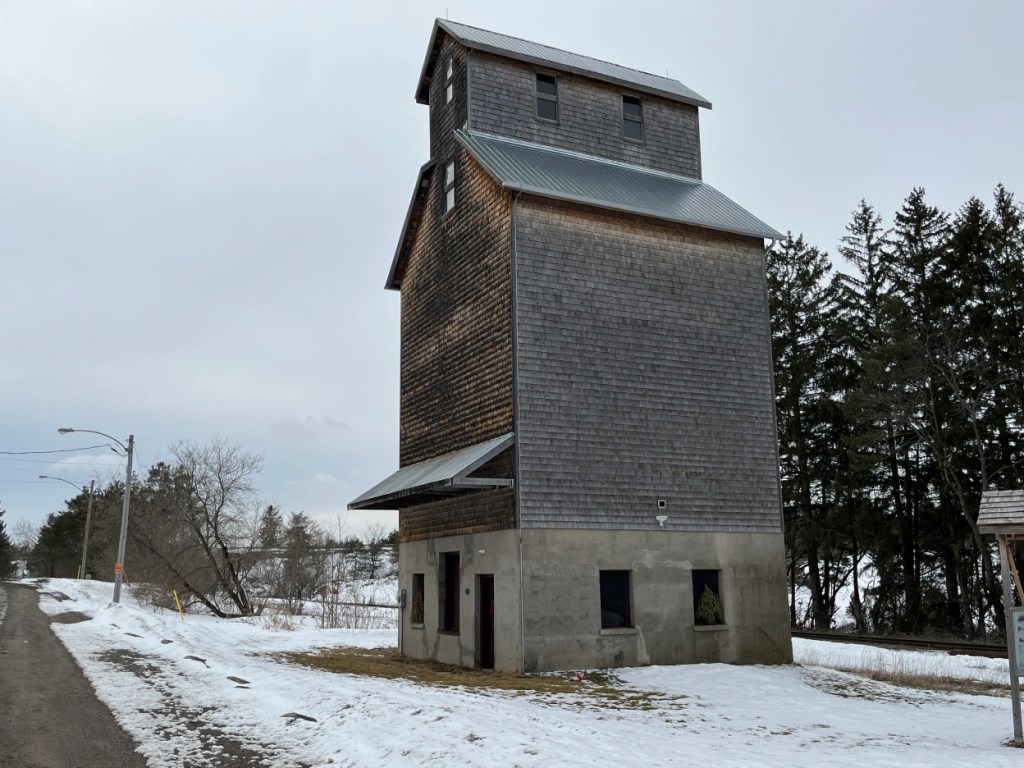
A grain elevator still exists within the city of Toronto on Dawes Road. When it comes to research on the internet it is easy to find conflicting information. Construction dates range to as early as the 1850s with 1890 also being a prominent date. The city’s land use maps suggest 1906. The land developers have to present a historic context in their proposals and they also claim it to be a 1906 wooden crib grain elevator and feed mill. The use of construction materials would suggest that the 1906 date is correct as the first-floor cement would not have come into popular use until after 1900. This elevator can be found at the following map link.

At one time almost every farm in Ontario had a silo beside the barn. Many of the barns have vanished but the concrete silos still dot the rural landscape. These were essentially private grain elevators that were used to store grain for feeding livestock.

Grain elevators come in many different shapes and sizes but they are slowing disappearing from the landscape.
Related stories: Pontypool Grain Elevator, Ireland Park with Bathurst Street Grain Elevator, Schomberg, Chalmer’s Milling Company, Abandoned Kirby Road
Like us at http://www.facebook.com/hikingthegta
Follow us at http://www.hikingthegta.com
Also, look for us on Instagram













