Feb.3, 2024
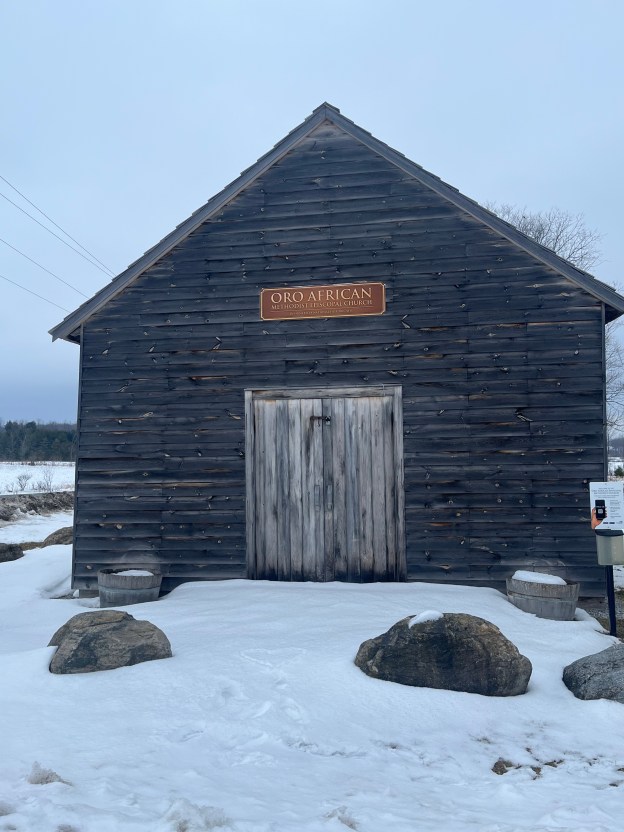
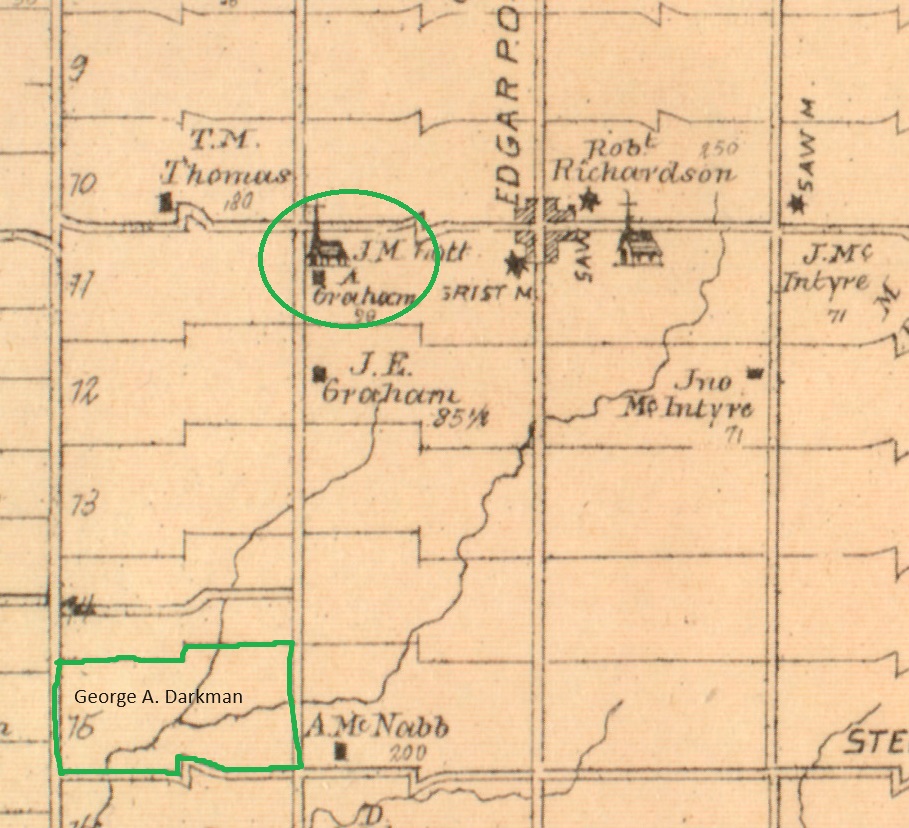
The Oro African Methodist Episcopal Church is a National Historic Site that was designated in 2000. It is the last remaining building in an African Canadian community that was developed in Oro Township between 1830 and 1850. The idea of such a community was first proposed in 1783 by Sir Guy Carlton who was the Commander-in-Chief of British forces in North America. It was thought that integrating African Canadians into a farming community would allow them to settle into a new life in British North America. Carlton had promised freedom to slaves of the American Revolutionaries who fought on the side of the British during the American War of Independence. Many of these people also fought during the War of 1812 under Captain Runchey’s Company of Coloured Men. The 1877 County Atlas image below shows the location of the church as well as a property owned by one of the members. In an apparent act of racism, only the white settlers names are recorded on the map and so I have marked the property of George A Darkman on it as he is featured in this story as an example of the individuals that made up the church. By the time of this map, it was no longer property of the family.
Between 1819 and 1826 twenty-five black men were granted 100 acre plots of land in Oro Township by the British. Eleven of these got their grants in acknowledgement of miliary services. Of these 25 only nine of them would take up their grants and these were along a section of land on Line 1 known as Wilberforce Road. This road was named after the British Abolitionist William Wilberforce who was a politician who fought in British Parliament for the abolishment of slavery in the British Empire. Between 1829 and 1831 another 30 families moved into the community.
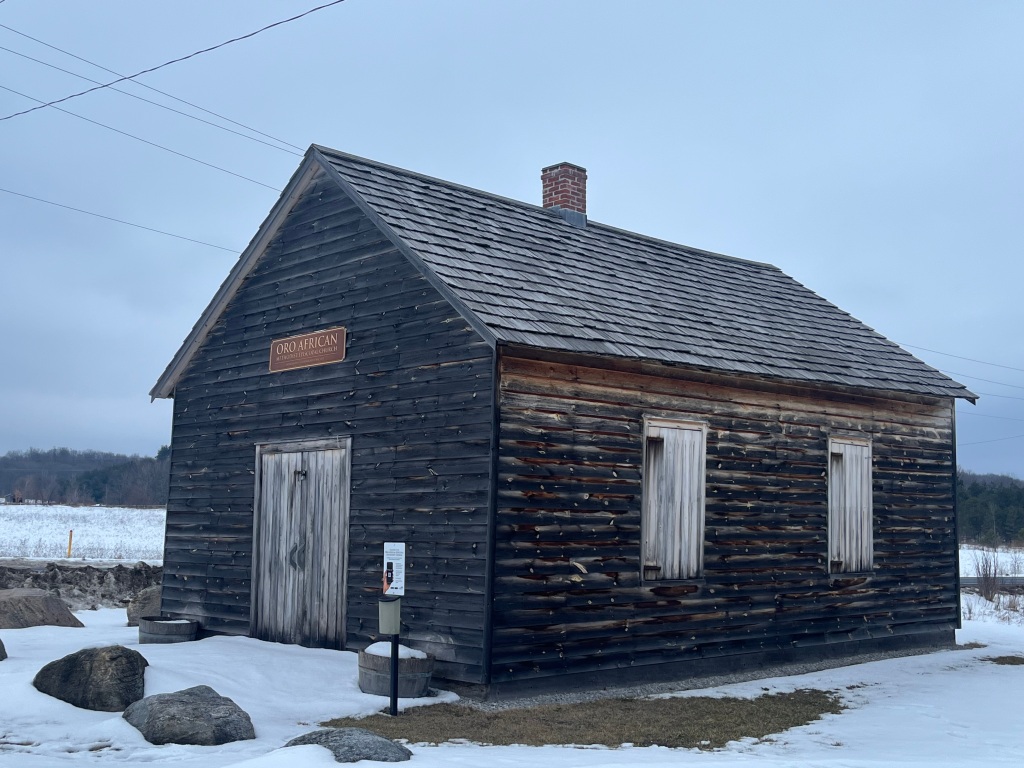

A one-acre parcel of land was acquired for use as a burial grounds and to build a church for the community. The church was built in 1849 out of hewn logs which were covered on the outside with clapboard about 10 years later to help keep out the wind and cold weather. By 1900 the community had declined as many of the settlers took advantage of Lincoln’s Emancipation Proclamation. This allowed former slaves to return to the USA and many of the settlers went in search of long lost family members. The British Methodist Episcopal Church declared the building abandoned in 1916 although services were continued until the 1920s.

The building fell into a state of disrepair and by 1947 it was in such poor condition that the local descendants of the original settlers feared that this piece of history would be lost. Efforts were made to restore it with further repairs being made in 1956 and again after vandalism in 1981 when two stolen dump trucks were smashed into the building leaving it seriously damaged.

One of the members of this church was simply known as George. He was born into slavery in Virginia sometime around 1769 and came to Canada prior to 1812. He was one of the soldiers who served in Captain Runchey’s Company of Coloured Men. White settlers were granted 200 acres but black ones were only given 100 acres. George petitioned for a land grant based on his service in the War of 1812 and was granted Lot 15 on concession 2 in Oro Township. In order to receive the land patent it was required that he have a full name and so displaying a sense of humour, he chose George A. Darkman. George left his property to his wife and two children who still lived in the USA and his will is recorded as being the first will to be probated in Oro Township. The will stated that his family had to come to the property within five years and sadly they never made it. Perhaps they were still enslaved themselves. The provision was made that if they didn’t come it would go to a white friend of George, and this is what transpired.

The church was declared a National Historic Site in 2000 but was still left to slowly deteriorate yet again. A cultural heritage assessment was conducted in 2013 and a preservation plan was put into place in 2015. The floor needed to be stabilized and the ceiling joists were reinforced. New cedar shingles were put on the roof and some of the clapboard was replaced. One of the most interesting discoveries during this restoration project was the fingerprint of one of the original settlers which was preserved in the plaster chinking between the logs.
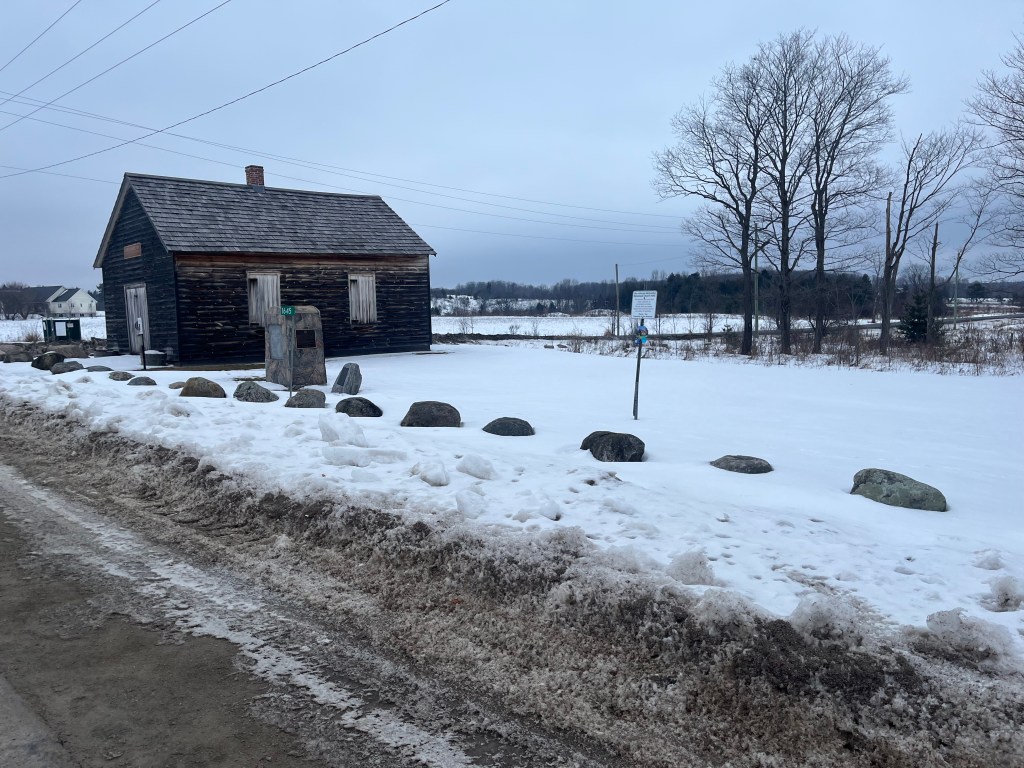

An unmarked graveyard lies in the south part of the property and a cairn was added in 1947 to identify the names of 24 families buried there.

This church is perhaps the oldest surviving log church from a black congregation in North America and it is fortunate that it has been preserved to help maintain the memory of this important chapter in our shared history. For further reading on early black settlers, see our feature on Griffin House. Also, enjoy our story about Turner Chapel, another African Methodist Episcopal Church.
Related Stories: Griffin House, Turner Chapel
Google Maps link: Oro African Methodist Episcopal Church
Like us at http://www.facebook.com/hikingthegta
Follow us at http://www.hikingthegta.com
Also, look for us on Instagram
















